Hello,
How Can We Help You?
Contact Form
Fill out the form and we will contact you as quickly as possible.
|

Native app development refers to the process of building apps for a specific platform using its official programming languages and tools. For instance, Swift or Objective-C is used for iOS, while Kotlin or Java is used for Android. Hybrid app development on the other hand involves creating apps using web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) that operate like native apps within a container. Native app development delivers a platform-optimized experience, whereas hybrid app development allows for app creation for iOS and Android with a single codebase. From a profitability perspective, both approaches have their pros and cons. Native apps provide higher performance and user satisfaction, while hybrid apps offer lower costs and faster development. For example, a native app can directly access the device’s hardware, resulting in faster performance. Hybrid apps, however, speed up the development process with cross-platform support. Businesses should choose between these two methods based on their project needs and goals.
Native app development has a clear edge over hybrid app development in terms of performance and user experience. Native apps have direct access to the device’s hardware and operating system, enabling a faster and smoother experience. For example, a gaming app developed natively delivers superior graphics performance and response times. Hybrid app development relies on web technologies, which introduces an intermediary layer that can lead to performance degradation. Especially in apps with complex animations or high computational requirements, hybrid apps may fall short. In terms of adhering to the design standards of iOS and Android platforms, native apps offer a better experience. iOS apps can follow Human Interface Guidelines, while Android apps can align with Material Design principles, both easily achieved through native development. From a profitability standpoint, native apps with higher user satisfaction can foster greater user loyalty, potentially leading to higher long-term revenue for the business.
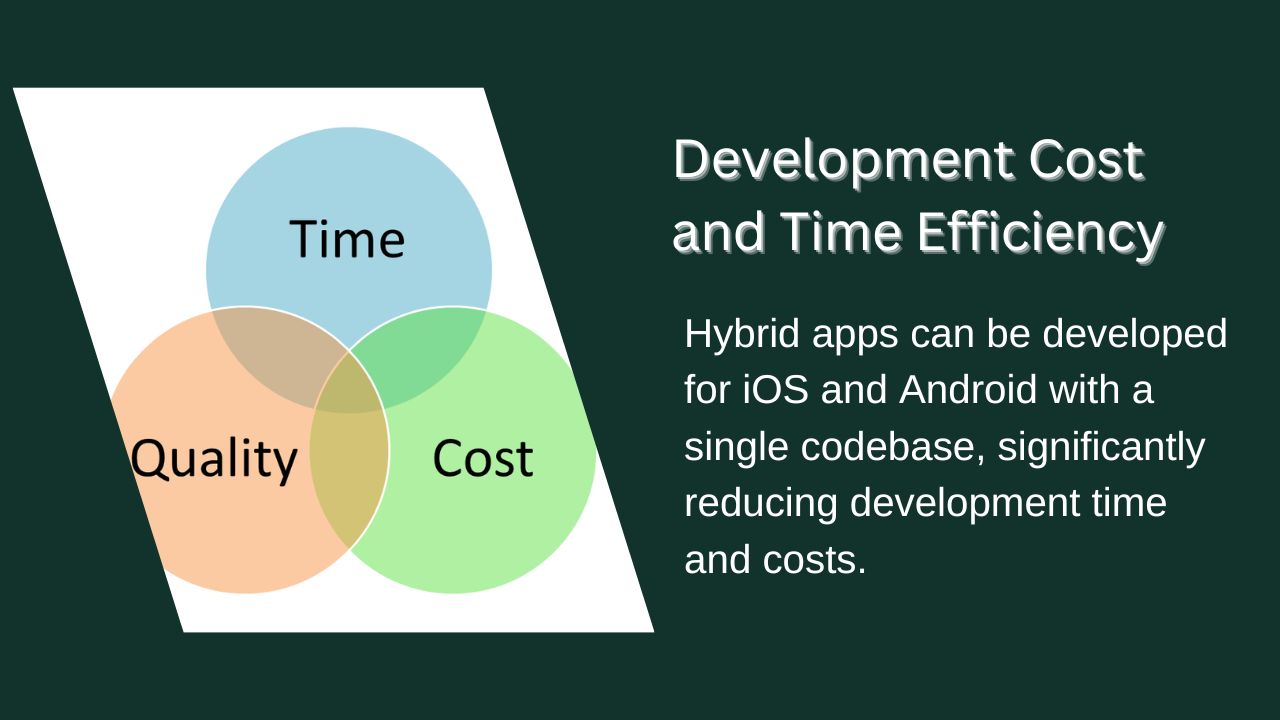
Hybrid app development holds an advantage over native app development in terms of development cost and time efficiency. Hybrid apps can be developed for iOS and Android with a single codebase, significantly reducing both development time and costs. For example, a developer can use a framework like React Native or Ionic to write code that works on both platforms. Native app development however, requires separate codebases for each platform, which means more time and resources are needed. Separate teams proficient in Swift for iOS and Kotlin for Android may be required. That said, native apps may incur lower maintenance costs in the long run since they adapt more quickly to platform updates. Hybrid apps, due to their cross-platform nature, can sometimes face platform-specific bugs, resolving which may lead to additional costs. From a profitability perspective, hybrid development is more suitable for low-budget projects, while native development offers a more sustainable solution for large and complex projects.
Native app development outperforms hybrid app development in accessing platform-specific features and offering flexibility. Native apps can directly interact with the device’s hardware and operating system, providing deep integration. For instance, features like Face ID, Apple Pay, or HealthKit on iOS, and NFC, sensors, or Google Fit on Android, are easily accessible with native development. Hybrid app development typically relies on bridges or plugins to access such features, which requires extra development effort and can sometimes result in performance losses. Quick access to the latest features of iOS and Android platforms is possible with native development, making the app more functional for users. In terms of flexibility, native development allows developers to perform platform-specific optimizations. From a profitability standpoint, native apps can attract more users by enhancing user experience with platform-specific features, potentially leading to higher revenue for the business.
Native app development and hybrid app development exhibit different dynamics in maintenance and update processes. Native apps adapt to platform updates more quickly since they are developed using the platform’s tools and languages. For example, when iOS or Android releases an update, native developers can immediately apply it, ensuring the app remains compatible. Hybrid app development however, depends on the framework used, and sometimes framework updates lag behind platform updates. This can lead to compatibility issues and additional maintenance costs. Native apps, using separate codebases for iOS and Android can be updated independently for each platform, offering more control. However, this process may require more time and resources. Hybrid apps can be updated more quickly since they use a single codebase. From a profitability perspective, native apps may offer an advantage for long-term projects by causing fewer maintenance issues.
Native app development can be more effective than hybrid app development in terms of marketing and user loyalty. Native apps offer high performance and a platform-specific user experience, encouraging users to engage with the app more frequently and remain satisfied. For example, an e-commerce app developed natively provides fast loading times and a seamless shopping experience, increasing the likelihood of repeat purchases. Hybrid app development enables reaching a broader audience quickly since a single app is developed for iOS and Android This offers a cost advantage in marketing, especially for startups. However, hybrid apps may lose user interest due to performance issues. From a profitability perspective, native apps generate more revenue through user loyalty, while hybrid apps can achieve short-term gains by reaching a wider audience at a lower cost.
Native app development and hybrid app development will continue to cater to different needs in the mobile app ecosystem. Native development will maintain its dominance in performance and access to platform-specific features. Technologies like AI, augmented reality, and 5G will further enhance the capabilities of native apps. For instance, an augmented reality app developed natively can fully leverage the device’s hardware. Hybrid app development continues to improve its performance, with frameworks like React Native and Ionic delivering better results. As iOS and Android platforms introduce new features, native development can adapt to these innovations more quickly. However, hybrid development will retain its popularity, particularly among small and medium-sized businesses, due to its cost efficiency and cross-platform support. From a profitability standpoint, businesses can increase both user satisfaction and revenue by choosing the method that best aligns with their project goals.
Contact Form
Fill out the form and we will contact you as quickly as possible.
 Notification Center 00:00
Notification Center 00:00